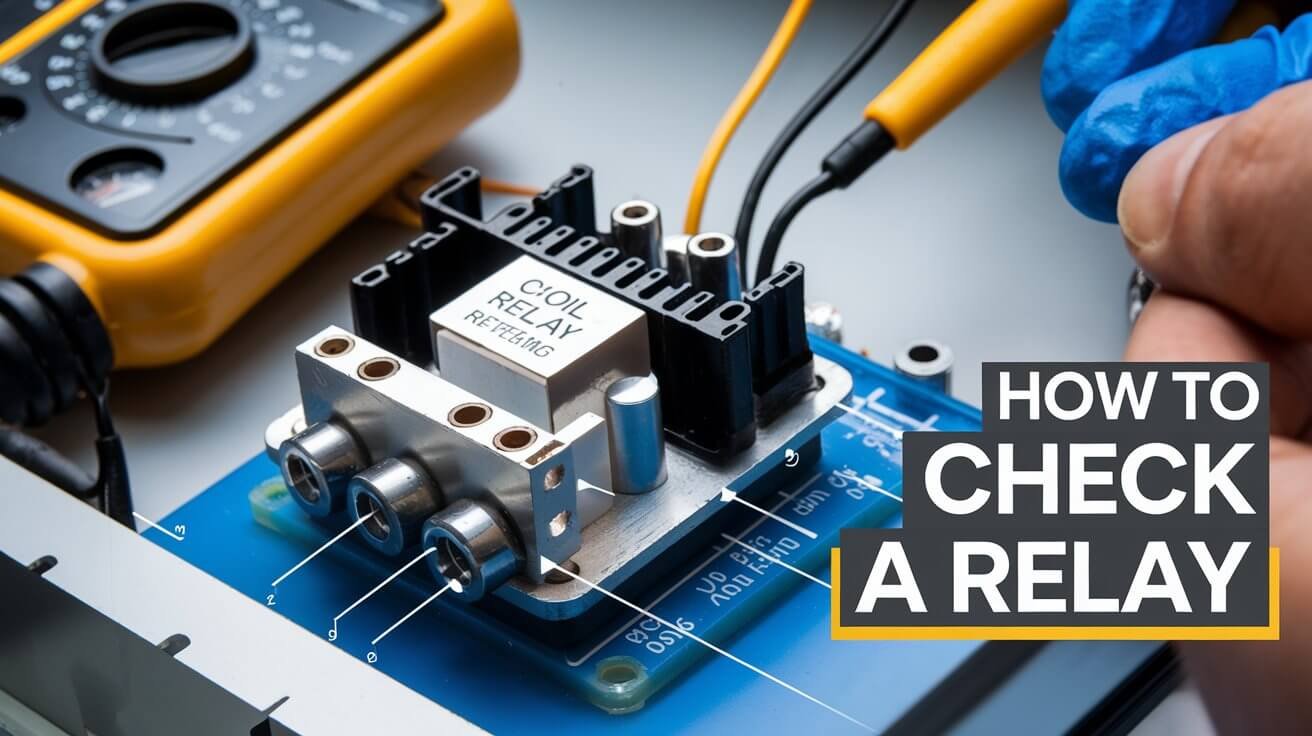
Relays are key in vehicles, managing high amperage circuits with low amperage ones. For example, a radiator fan can use up to 25 amps. If these relays fail, it can lead to electrical problems. Knowing how to test relays is essential for fixing these issues.
By learning to test and maintain relays, you can avoid electrical damage. This ensures your vehicle’s accessories work right. Whether it’s a faulty radiator fan or another issue, knowing how to troubleshoot can help you fix it fast. With the right tools and knowledge, you can manage your vehicle’s electrical system well.
Relay Basics and Functions
Relays are key in many electrical systems. Knowing how they work is vital for fixing problems. A relay has four pins: 85, 86, 87, and 30. Each pin has a special job.
The coil, controlled by pins 85 and 86, turns the relay on. Pins 30 and 87 then switch power on a circuit.
There are different relays, like 4-pin and 5-pin ones. A 4-pin relay controls one circuit. A 5-pin relay switches power between two circuits. The coil, armature, contacts, and terminals help the current flow.
Basic Relay Components
The coil uses 24 VDC to turn the magnet on. The contacts switch power on a circuit or between two circuits.
Common Relay Types
There are many relay types, like normally open (SPST) and change-over (SPDT) relays. These relays have resistor protection in 12V or 24V. Knowing about these types helps spot and fix problems.
Signs of Relay Problems
Watch for signs of relay trouble. Look for arcing, pitting, and increased resistance. Regular checks can prevent failures and keep the system reliable.
When working with relays, remember the max temperature, dropout voltage, and endurance. Knowing these basics helps you test and fix relays. This ensures your electrical system works well.
| Relay Type | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 4-pin relay | Controls a single circuit | Automotive, industrial control systems |
| 5-pin relay | Switches power between two circuits | Automotive, power distribution systems |
Required Tools for Relay Testing
To test a relay, you need a few key tools. These include a multimeter, power supply, and test leads. A benchtop power supply gives a steady voltage. A multimeter is used to check voltage, resistance, and if there’s a connection. Test leads, like alligator clips, connect the multimeter to the relay.
Choose a digital multimeter for its accuracy and many functions. It should measure DC and AC voltage, resistance, and continuity. A power supply with adjustable voltage and current is important for safe testing. Also, get high-quality test leads that last long and connect well.
- A benchtop power supply for providing a stable voltage source
- A multimeter for measuring voltage, resistance, and continuity
- Test leads, such as alligator clips, for connecting the multimeter to the relay
With these tools, you can do many tests. From simple checks to detailed voltage and resistance tests. Whether you’re a pro electrician or a DIY fan, the right tools ensure you get accurate results. Testing relays with a multimeter and power supply is easier with good test leads.
Safety Precautions Before Testing
Working with electrical parts needs careful attention to safety. Before you test a relay, make sure you’re safe and the part is ready. Always disconnect power first to avoid shocks or power surges.
It’s also important to work in a safe place. Stay away from flammable liquids or gases. Make sure your area is well-ventilated and free from dangerous materials.
Power Disconnection Steps
To keep safe, follow these steps to disconnect power:
- Switch off the power supply to the relay
- Check with a multimeter that the power is off
- Wait a few minutes for any leftover power to go away
Workplace Preparation
Get your workspace ready by:
- Removing any flammable stuff or liquids
- Ensuring good air flow
- Wearing protective gear like gloves and safety glasses
Personal Protection Equipment
Wearing the right gear can protect you from injury. Use gloves and safety glasses made for electrical work. They add an extra layer of safety.
| Protective Gear | Description |
|---|---|
| Gloves | Insulated gloves to prevent electrical shocks |
| Safety Glasses | Protective eyewear to prevent eye injuries |
How To Check A Relay With a Multimeter
To check a relay with a multimeter, you need to do a few tests. First, set your multimeter to measure resistance. Then, touch the probes to the electromagnetic coils, usually pins 85 and 86. A normal reading should be between 50 and 120 ohms.
Next, do a continuity test. Set your multimeter to the continuity test mode. Touch the probes to the switch pins, usually 87 and 30. If the relay works right, you’ll hear a beep or see a low resistance reading. This shows the circuit is complete.
Here are the steps to follow for multimeter testing:
- Set your multimeter to resistance measurement mode.
- Measure the resistance between the electromagnetic coils (pins 85 and 86).
- Perform a continuity test between the switch pins (87 and 30).
- Verify that the relay makes an audible click when the electromagnetic coil is energized.
Following these steps and using your multimeter, you can check if your relay is working. Always check your vehicle’s repair manual for specific instructions. The process might differ based on the relay type and its use.
| Test | Expected Result |
|---|---|
| Resistance between electromagnetic coils (pins 85 and 86) | 50-120 ohms |
| Continuity test between switch pins (87 and 30) | Low resistance or beep |
Visual Inspection Methods
Starting a relay inspection with a visual check is key. It helps spot physical damage, corrosion, and other issues. A good visual inspection can show clear signs of relay failure, like cracked cases or loose terminals.
Looking for physical damage is a big part of the visual check. You should look for wear and tear signs like scratches, dents, or rust. Also, check the terminals for corrosion or damage. Corrosion can stop the relay from working right.
Physical Damage Assessment
When assessing physical damage, check the relay’s case for cracks or breaks. Also, inspect the terminals for any damage or corrosion. This is important to find any issues that might affect the relay’s performance.
Corrosion Detection
Corrosion detection is a critical part of the visual inspection. Look at the relay’s terminals and contacts for corrosion or rust. This helps spot problems that could affect the relay’s performance.
Connection Quality Check
Lastly, check the connections between the relay and other parts. Look for any damage or corrosion on the wires and terminals. Good connections are vital for the relay to work right, and any problems can be found here.
Following these steps, you can do a detailed visual inspection of the relay. This helps find problems early and prevents bigger issues. Regular checks and maintenance keep the relay reliable and prevent system problems.
| Inspection Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Damage Assessment | Check the relay’s case for cracks or breaks, and inspect the terminals for damage or corrosion. |
| Corrosion Detection | Check the relay’s terminals and contacts for signs of corrosion or rust. |
| Connection Quality Check | Inspect the wires and terminals for signs of damage or corrosion. |
Direct Power Testing Techniques
Understanding the basics of relay activation is key when testing power directly. This means energizing the coil pins, usually labeled as 85 and 86 on a 4-pin relay. As the coil is energized, you’ll hear a click, showing the relay works right.
To start testing power, make sure you have the right power source. Relays need specific voltages, like 5V or 12V. Also, check the relay’s ratings for maximum voltages and currents. Always use safety gear and a multimeter to check the coil’s resistance and continuity.
Some important things to remember during direct power testing include:
- Using a power supply that matches the relay’s specifications
- Checking the coil resistance between 40Ω to 120Ω
- Testing for continuity between COM-NC and COM-NO terminals
- Listening for the audible click test during relay activation
Following these steps and understanding power supply testing and relay activation, you can test a relay effectively. This ensures it’s working as it should.
| Relay Type | Coil Voltage | Maximum Current |
|---|---|---|
| 5V Relay | 5V DC | 10A |
| 12V Relay | 12V DC | 10A |
Resistance Testing Procedures
Testing relays is key, and resistance testing is a big part of it. You use a multimeter to check the coil and contact resistance. First, set your multimeter to ohms and touch the leads to the coil terminals. A good coil should have a resistance between 50 and 120 ohms.
If the reading is outside this range, it might mean a coil winding problem. Contact point testing is also vital. You measure the resistance between the NC and NO terminals and the common terminal. When the relay is off, the NC terminal should have nearly zero resistance to the common terminal. The NO terminal should have infinite resistance to the common terminal. Any other reading could mean a contact problem.
Coil Resistance Measurement
To measure the coil resistance, follow these steps:
- Set your multimeter to the ohms function
- Touch the leads to the coil terminals
- Take note of the reading and compare it to the expected value
If the reading is outside the expected range, it might mean a coil winding problem. Regular coil testing can help spot issues before they cause failures.
Contact Point Testing
Contact point testing involves measuring the resistance between the NC and NO terminals and the common terminal. This can be done using a multimeter and following these steps:
- Set your multimeter to the ohms function
- Touch the leads to the NC and common terminals
- Take note of the reading and compare it to the expected value
- Repeat the process for the NO and common terminals
Following these steps and using a multimeter, you can make sure your relay works right. You can also spot any issues before they cause problems.
| Test | Expected Value | Indication of Problem |
|---|---|---|
| Coil Resistance | 50-120 ohms | Coil winding problem |
| NC Terminal Resistance | Nearly zero | Contact problem |
| NO Terminal Resistance | Infinite | Contact problem |
Common Relay Problems and Solutions
Identifying common relay problems and their solutions is key. Troubleshooting relays is vital to fix issues. Poor contact issues often lead to relay failures. Cleaning contacts can solve problems with worn-out contacts.
Coil replacement is another fix for common relay issues. Coil failure is a big reason for relay problems. Replacing the coil can fix the relay and prevent more damage. Temperature and load current also impact relay operation.
Poor Contact Issues
Poor contact issues stem from overheating and contact welding. Regular maintenance, like cleaning and inspecting contacts, is essential. This helps prevent failures and keeps the relay working well.
Coil Failure Fixes
Coil failure is often due to electromagnetic issues, which cause 66% of relay failures. To fix it, replace the coil or troubleshoot the relay. Fixing coil failure prevents more damage and keeps the relay running smoothly.
| Common Relay Problems | Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Poor Contact Issues | Contact Overheating, Welding of Contacts | Contact Cleaning, Inspection |
| Coil Failure | Electromagnetic Component Issues | Coil Replacement, Relay Troubleshooting |
Relay Replacement Guidelines
Replacing a faulty relay is often the simplest fix. But, it’s key to find a compatible replacement to keep your electrical system working right. We’ll share tips on how to install the right relay and choose the best one.
Relays are usually affordable, but finding a match can be tough. Omron’s G8P series was stopped due to low sales, making finding a direct replacement hard. It’s important to look at the housing, mounting, and wiring of any replacement you consider.
Here are some key things to think about for a successful relay swap:
- Matching specifications: Make sure the new relay matches the old one in voltage, current, and contact type.
- Proper installation techniques: Always follow the manufacturer’s installation guide to avoid damage.
- Regular testing: Use a multimeter to test the relay often to catch any issues early.
Keeping these tips in mind and understanding your system’s needs, you can make a relay swap that works well. Always install the relay correctly and test it before using it to ensure it works perfectly.
| Relay Type | Specifications | Installation Tips |
|---|---|---|
| PCB Power Relay | Voltage: 12V, Current: 10A, Contact Configuration: SPST | Mount the relay on a heat sink, and ensure proper wiring to avoid short circuits. |
| General Purpose Relay | Voltage: 24V, Current: 5A, Contact Configuration: SPDT | Use a relay socket to simplify installation and reduce the risk of damage to the relay or surrounding components. |
Final Thoughts
Checking and maintaining your car’s relays regularly is key to keeping its electrical system healthy. Relay failures can really mess up your car’s performance. They might even cause the system to fail completely.
By following the steps in this guide, you can spot and fix problems early. This keeps your car’s electrical parts working well. It’s a smart way to avoid big issues.
Regular relay checks make your car safer and last longer. You can find problems with simple tests like looking, measuring resistance, and testing power directly. Fixing or replacing the relay terminal block can solve many issues.
This DIY approach saves you time, money, and stress. It helps avoid unexpected car troubles.
Even with this guide, sometimes you might need a pro’s help. If you’re not sure or face a big problem, get a car expert’s advice. They can help keep your car’s electrical system in top shape.
Frequent Questions
What are the core components of a relay and how do they work together?
A relay has a coil, contacts, and a switch mechanism. The coil makes a magnetic field when powered. This field turns the switch on, letting current flow through the contacts.
This setup lets relays control big electrical circuits with just a small signal.
What are some common signs that a relay might be failing?
Signs of a failing relay include clicking sounds and flickering lights. You might also see electrical problems like parts failing or working only sometimes. Look for physical damage or corrosion on the relay.
What essential tools are needed to effectively test a relay?
You’ll need a multimeter, a power supply, and test leads. The multimeter checks resistance, continuity, and voltage. The power supply turns the relay on for testing.
If you don’t have the right tools, a 12V battery can work too.
What safety precautions should be taken before testing a relay?
Always disconnect the car’s battery first. This keeps the electrical system safe. Work in a clean, well-lit area and wear gloves for safety.
How can a multimeter be used to check the functionality of a relay?
Use the multimeter to check coil resistance and contact continuity. Make sure the relay switches on when powered. This helps find and fix any problems.
What should I look for during a visual inspection of a relay?
Look for damage, corrosion, and good electrical connections. Check for overheating, a cracked housing, and oxidation. Make sure connections are tight and clean.
How can I test a relay using a direct power source?
Connect a 12V battery or power supply to the relay’s coil. This turns the relay on. You should hear a “click” and see the contacts switch.
What are the typical resistance values I should expect when testing a relay?
A good coil should have 30-100 ohms of resistance. Contact resistance should be very low. If these values are off, the relay might have a problem.
What are some common relay problems and how can they be addressed?
Relay problems include bad contacts and coil failures. Clean the contacts, replace the relay, or fix electrical issues to solve these problems.
How do I properly replace a faulty relay?
Choose a relay that matches the original’s specs. Make sure it’s installed right and connections are secure. Follow the manufacturer’s guide for a successful swap.




