A car fuse is a small part that protects the car’s electrical system. It cuts off electricity when there’s too much or a short circuit. Knowing how to spot a blown fuse is key for car owners. It helps avoid damage to the electrical system and keeps your car running well.
A blown fuse can cause many problems. It might just make your interior lights not work. Or it could stop your car from starting. This shows how important the car fuse is for the electrical system.
Dealing with a blown fuse is common in car maintenance. Being able to find and replace it can save you time and money. The car fuse is vital for protecting the electrical wiring from too much current or short circuits. It’s important to know how to spot and replace a blown fuse, whether it’s a 15 amp or 25 amp fuse.
Car Fuse Basics and Their Function
Automotive fuses, also known as car fuses, protect a vehicle’s electrical wiring from overcurrents and short-circuits. They come in different shapes and sizes, with blade-type fuses being the most common. Knowing about the various types of automotive fuses and their roles is key for vehicle owners. It ensures their safety and the proper working of their car’s electrical systems.
The main job of a fuse is to prevent damage to a vehicle’s electrical wiring and components. When a fuse blows, it cuts off the circuit, stopping further damage. There are several types of automotive fuses, including plug-in, glass tube, and cylindrical fuses. Each type is designed to protect specific electrical circuits in a vehicle.
Types of Car Fuses
- Plug-in fuses: The most common type of fuse in cars, identified by different colors representing various current sizes.
- Glass tube fuses: A cylindrical type of fuse with a glass exterior and metal end caps, once common but now rare.
- Cylindrical fuses (PAL fuse): Larger than plug-in fuses and suitable for high current circuits like power windows or heaters.
Knowing about the different types of automotive fuses and their functions helps vehicle owners identify and replace blown fuses. This ensures their safety and the proper functioning of their car’s electrical systems. Fuse boxes are usually found under the bonnet, dashboard, or in the boot. Understanding car fuses is essential for any vehicle owner. It helps prevent electrical problems and ensures a safe and smooth driving experience.
| Fuse Type | Description | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| Plug-in fuse | Most common type of fuse in cars | Interior lights, radio, turn signals |
| Glass tube fuse | Cylindrical type of fuse with glass exterior | Older vehicles, rare in modern cars |
| Cylindrical fuse (PAL fuse) | Larger than plug-in fuses, suitable for high current circuits | Power windows, heaters, high current systems |
Signs Your Car Has a Blown Fuse
A blown car fuse can lead to various electrical problems. These issues might seem small at first but can get worse. Signs include lights that don’t work right or accessories that don’t turn on.
Common signs of a blown fuse include problems with lights, the radio, and climate control. A warning light on the dashboard or a burned smell can also indicate a blown fuse. It’s important to fix these issues quickly to avoid more damage.
To spot a blown fuse, knowing why they blow is key. Issues like faulty switches or wires can cause a fuse to blow. Recognizing these signs helps car owners fix problems before they get worse.
- Avoid overloading power sockets to prevent blowing a fuse
- Use high-quality accessories to reduce the risk of electrical issues
- Regularly inspect the fuse box and electrical components to identify possible problems
Knowing the signs and taking steps to prevent problems can help. If a fuse is blown, replace it with a new one of the same type and amperage rating. This prevents further damage to your car’s electrical system.
Car Fuse Box Location and Access
To find your car’s fuse box, look for it in common spots. It’s usually under the hood, near the steering wheel, or under the dashboard. You might also find it beneath the back seats or in the boot. The main box is often under the steering wheel, with secondary panels elsewhere.
Check your car’s manual for the fuse box’s exact spot. The manual will have a fuse diagram. This diagram is key for finding blown fuses.
Main Fuse Box Positions
The main fuse box is often under the steering wheel or in the engine. You might need to remove a cover to get to it. Once you find it, you can start looking for the blown fuse.
Secondary Fuse Panels
Some cars have extra fuse panels. These can be under the dashboard or beneath the back seats. They control things like the radio or air conditioning.
Reading Your Vehicle’s Fuse Map
Understanding your fuse diagram is vital. It shows where each fuse is and what it controls. This way, you can quickly find and replace a blown fuse.
Always check your manual for fuse box access tips. With the right info, you’ll be able to find and fix fuses easily. This keeps your car running well.
| Fuse Box Location | Description |
|---|---|
| Under the steering wheel | Main fuse box, usually contains the most important fuses |
| Under the dashboard | Secondary fuse panel, may contain fuses for specific systems |
| Beneath the back seats | Secondary fuse panel, may contain fuses for specific systems |
| In the boot | Some vehicles may have a fuse box located in the boot |
Tools Required for Fuse Testing
To test car fuses, you’ll need a few key tools. A fuse puller is great for safely removing fuses. A multimeter helps measure a fuse’s resistance. A test light is handy for fast checks. These tools help spot blown fuses and fix your vehicle.
When using a multimeter, place the fuse on a non-conductive surface like wood or plastic. This ensures accurate readings and avoids damage. You can use different Ohm settings on the multimeter to measure the fuse’s resistance.
Some common tools for fuse testing include:
- Fuse puller: for safe removal of fuses
- Multimeter: for measuring resistance and voltage
- Test light: for quick checks of fuse integrity
With these tools, you can easily find and fix blown fuses. This gets your vehicle running smoothly again.
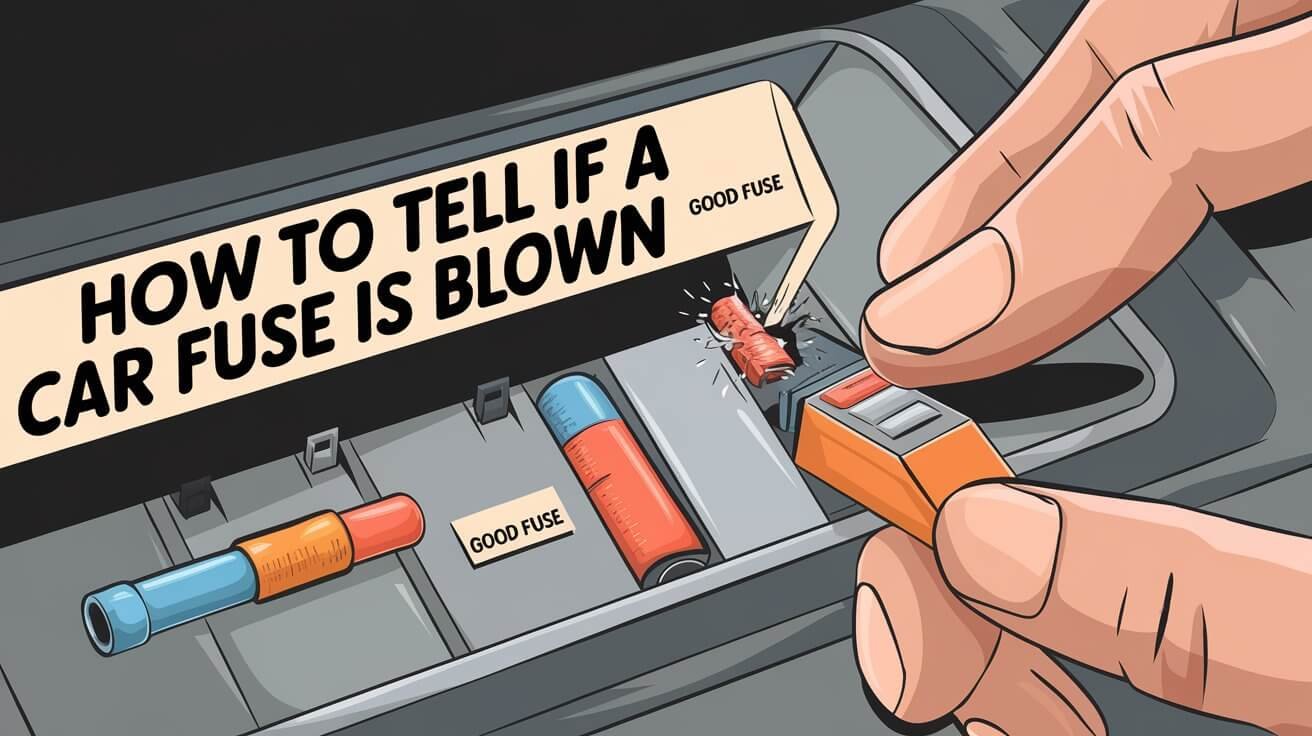
How To Tell If A Car Fuse Is Blown – Visual Inspection Method
Checking a car fuse is easy and effective. Look for damage or wear on the fuse, like a broken or burnt look. First, find the fuse box in your car and pick the fuse you want to check. Then, take out the fuse and hold it up to light.
Color Indicators
Look at the fuse colors. A blown fuse might look discolored or cloudy. If it has a metal strip, see if it’s broken or melted. A broken fuse will show a gap in the metal strip.
Metal Strip Assessment
Check the metal strip inside the fuse. A good fuse has a continuous strip. A blown fuse has a broken or discontinuous strip. Also, check if the fuse colors match the manufacturer’s specs. If they don’t, it might be a faulty or blown fuse.
Some common signs of a blown fuse include:
- A broken or burnt appearance inside the translucent body
- A discolored or cloudy appearance
- A broken or melted metal strip inside the fuse
- A visible gap in the metal strip
Doing a visual check, you can quickly find out if a car fuse is blown. Always replace it with the right amperage rating to protect your car’s electrical system.
| Fuse Type | Color Indicator | Metal Strip Condition |
|---|---|---|
| Good Fuse | Match manufacturer’s specifications | Continuous metal strip |
| Blown Fuse | Discolored or cloudy appearance | Broken or discontinuous metal strip |
Testing Fuses With a Multimeter
To find out if a car fuse is blown, you can use a multimeter. This method is a bit more technical but gives a clear answer. First, set the multimeter to 20K ohms. Then, touch both sides of the fuse with it.
If the fuse is good, the multimeter will show a reading close to 0 ohms. This means the fuse is working right.
A multimeter can also check if there’s continuity between the fuse’s two pins. If there’s no continuity, the fuse is blown. This test is handy when you’re unsure if a fuse is blown or not.
Using a multimeter, you can see the fuse’s resistance. This helps you know if it needs to be replaced.
Here are the steps to follow for multimeter testing:
- Set the multimeter to the ohms setting
- Touch the multimeter leads to both sides of the fuse
- Check the reading on the multimeter. If it shows 0 ohms or close to 0, the fuse is good. If it shows infinity, the fuse is blown
Testing fuses with a multimeter regularly can prevent big electrical problems. It’s also key to use the right fuse size and amperage for your car’s electrical system. By using a multimeter for ohms measurement and checking for fuse continuity, you can keep your car’s electrical system running smoothly.
Common Causes of Blown Fuses
Blown fuses can be really frustrating for car owners. But knowing why they happen can help avoid them in the future. Fuses can blow for many reasons, like too much current, short circuits, or wiring issues. Finding out why a fuse blew is key to avoiding more damage to your car’s electrical system.
Short circuits can be caused by many things, like faulty electrical devices or wires exposed to moisture. Using too many accessories or the wrong fuse amperage can also blow fuses. Always use the right fuse amperage to avoid more electrical problems. If you’re not sure, it’s best to ask an auto expert for advice.
Electrical Overload Situations
When too many accessories use the same circuit, it can overload and blow a fuse. To prevent this, spread out the load and use the right fuse amperage.
Short Circuit Examples
A short circuit happens when electricity finds an unintended path, blowing a fuse. This can be due to faulty devices, corroded wires, or exposed conductors. Checking your car’s wiring and electrical parts regularly can spot problems before they cause a blown fuse.
Aging Wiring Issues
Old wiring can also lead to blown fuses. Wires can corrode, get damaged, or wear out over time, causing electrical problems. Keeping up with regular maintenance and inspections of your car’s wiring can help prevent blown fuses and keep your electrical system working right.
Fuse Replacement Steps
To replace a blown fuse, start by turning off the vehicle. Then, find the fuse box. Check your vehicle’s manual to locate it and spot the blown fuse. Always use a fuse with the same amperage rating to avoid electrical problems.
Here are the steps to follow for a new fuse installation:
- Turn off the vehicle and engage the parking brake.
- Locate the fuse box and refer to the diagram to identify the blown fuse.
- Remove the blown fuse carefully and inspect it for damage.
- Replace the blown fuse with a new one of the same amperage rating.
- Test the component to ensure proper functionality.
Choosing the right fuse amperage is key. A fuse with too high an amperage can cause bigger problems. A fuse with too low an amperage might blow again. By following these steps and using the correct fuse, you can safely replace a blown fuse.
Always check your vehicle’s manual for specific fuse replacement instructions. The process can vary by make and model. If you’re unsure or uncomfortable, consider getting help from a professional mechanic.
Safety Precautions During Fuse Testing
Working with car fuses requires electrical safety to avoid damage or injury. It’s key to turn off the vehicle and sometimes disconnect the battery before starting. This step prevents short circuits and electrical shocks.
Wearing protective gear like gloves and safety glasses is also important. Knowing how to safely disconnect the battery is critical to protect the vehicle’s electrical system.
Essential Safety Gear
- Gloves to prevent electrical shock
- Safety glasses to protect eyes from debris
- A multimeter to test fuses and electrical components
Battery Disconnect Procedures
Always disconnect the battery before working on the fuse box to avoid short circuits. Find the negative terminal and remove the cable. Following these steps and using protective gear ensures a safe fuse testing experience. It keeps the electrical system safe and prevents damage to the vehicle.
Multiple Blown Fuses – What This Means
Seeing multiple blown fuses in your car can signal serious electrical problems. These issues might need a pro to figure out and fix. If you notice many fuses blowing, fixing it fast is key to prevent more damage.
Blown fuses often point to bigger problems like short circuits or too much electrical load. To find the problem, you might need a multimeter. If you’re not sure how to use it, a mechanic can help you out.
Circuit Problems
Circuit issues can cause many fuses to blow. For instance, a loose bulb filament can mess with other circuits. Finding and fixing the problem is essential to stop more fuses from blowing.
When to Contact a Professional
If you keep having fuse problems, it’s time to get a pro’s help. A mechanic can check your car’s electrical system and fix it right. They can also spot future issues, saving you money and time.
| Symptom | Possible Cause | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Multiple blown fuses | Electrical system issues, complex problems | Seek professional diagnosis and repair |
| Circuit problems | Short circuits, electrical overload | Use a multimeter to test the fuses and identify issues |
| Recurring issues with blown fuses | Underlying component issues | Contact a professional mechanic for diagnosis and repair |
Preventing Future Fuse Issues
Regular electrical maintenance is key to avoiding future fuse problems. It means checking your vehicle’s electrical system often and not overloading circuits. This approach saves you time, money, and stress in the long run.
Electrical maintenance includes looking at the fuse box, spotting wear or damage, and swapping out fuses when needed.
Fuse protection is also vital to avoid circuit overload. This can be done by using top-notch accessories and not overloading power sockets. Also, picking the right fuse amp rating helps prevent failures and dangers. Some important tips to avoid future fuse problems are: * Don’t overload circuits with too many devices * Use quality accessories * Regularly check your vehicle’s electrical system * Replace fuses with the same size and amp rating * Fix any electrical problems quickly to avoid more damage
Sticking to these tips and focusing on electrical maintenance, you can stop future fuse problems. This ensures your vehicle’s electrical system works well. Remember, regular maintenance and fuse protection are key to avoiding circuit overload and other electrical issues.
| Preventative Measure | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Regular electrical maintenance | Prevents future fuse issues, saves time and money |
| Fuse protection | Prevents circuit overload prevention, ensures safe operation |
| Using high-quality accessories | Prevents damage to electrical system, ensures reliable operation |
Conclusion
Knowing how to find and fix blown fuses is key for car owners. You can spot and fix electrical problems in your car by learning about fuse types, where they are, and how to tell if one is bad. Simple steps like looking for blown fuses, using a multimeter, or replacing them can keep your car running well.
While some electrical issues need a pro, you can handle many fuse problems yourself. By following the advice in this article, you can manage your car’s electrical system. This way, you avoid serious issues like fires that can happen if you ignore electrical problems.
Common Queries
What is the purpose of car fuses?
Car fuses protect the electrical system from damage. They prevent overloads and short circuits.
What are the different types of car fuses?
There are mainly blade fuses. They come in various amperage ratings for different circuits.
How can I tell if a car fuse is blown?
If your car’s electrical parts don’t work, like the radio or headlights, it might be a blown fuse.
Where is the fuse box located in my car?
The main fuse box is usually under the dashboard or in the engine. Secondary panels might be elsewhere.
What tools do I need to test and replace car fuses?
You’ll need a fuse puller, a multimeter, and a test light. But, many issues can be seen with the naked eye.
How do I visually inspect a car fuse to determine if it’s blown?
Check the fuse’s color and the metal strip inside. If it’s broken or melted, it’s blown.
How can I use a multimeter to test a car fuse?
Use the multimeter to check for continuity. This can confirm if a fuse is blown more accurately than just looking.
What common issues can cause car fuses to blow?
Overloads, short circuits, and old wiring are common reasons for blown fuses.
How do I properly replace a blown car fuse?
Use a fuse with the right amperage rating. Remove the old fuse safely and install the new one correctly.
What safety precautions should I take when testing or replacing car fuses?
Turn off the car, wear safety gear, and sometimes disconnect the battery to avoid electrical dangers.
What does it mean if I find multiple blown fuses in my car?
Finding many blown fuses suggests a bigger problem. You might need a pro to find and fix the issue.
How can I prevent future car fuse problems?
Keep the electrical system in check, avoid overloading, and fix issues quickly to prevent fuse problems.