Relays are key in electrical systems. They control high-current circuits with low-current signals. Testing relays is vital for electrical diagnostics. We’ll cover the basics and advanced techniques to help you solve relay problems.
Testing relays is essential for fixing electrical issues in many areas. This includes cars, bikes, home automation, and appliances. Knowing how to test a relay helps you find and fix problems like blown fuses or circuit breakers. It’s a critical skill for electrical diagnostics and relay testing.
Basic Relay Functions and Components
A typical relay has several key parts. These include the electromagnetic coil, contact points, and control circuit elements. Knowing these parts is key for testing relays well. The electromagnetic coil creates a magnetic field when current flows through it, activating the relay.
The contact points switch the circuit on and off. In a 4-pin relay, pins 85 and 86 control the coil. Pins 30 and 87 switch the power. The contact points can handle specific currents, like 35A at 14VDC for normally open terminals.
Electromagnetic Coil Components
The electromagnetic coil is vital for the relay’s operation. It’s made of wire winding around a core. You can check its resistance to see if it works right.
Contact Points and Switching Mechanism
The contact points switch the circuit. They are made of normally open and normally closed contacts. When energized, they let current flow through the circuit.
Control Circuit Elements
The control circuit elements manage current to the coil. They include a resistor, capacitor, and diode. These work together to control voltage and current to the coil.
| Relay Type | Pin Configuration | Current Rating |
|---|---|---|
| 4-pin relay | 85, 86, 30, 87 | 35A at 14VDC (N/O), 20A at 14VDC (N/C) |
| 5-pin relay | 85, 86, 30, 87, 87A | 30A at 14VDC (N/O), 25A at 14VDC (N/C) |
Safety Precautions Before Relay Testing
Working with electrical parts requires electrical safety to avoid accidents. Before you test a relay, it’s key to take precautionary measures. This means setting up a safe space, handling tools with care, and wearing protective gear.
A safe area has no flammable liquids or gases. It should also have all electrical parts well-insulated. Make sure your tools work well and you know the relay’s parts and how they work. These steps help make your workspace safe for testing relays and lower the risk of electrical dangers.
Important safety precautions for working with relays include:
- Avoid working in environments with flammable liquids or gases
- Use proper insulation and protective equipment when handling electrical components
- Ensure all tools are in good working condition and properly calibrated
- Follow proper procedures for testing and handling relays to prevent damage or injury
Following these electrical safety tips and taking the right precautionary measures, you can have a safe and successful relay test. Always put electrical safety first when working with electrical parts. Never take risks that could harm you or others.
Required Tools for Relay Testing
To test a relay, you need the right tools. A digital multimeter is key for measuring voltage, current, and resistance. Look for a multimeter with good accuracy, resolution, and sampling rate.
A reliable power supply is also vital. It gives the relay the voltage and current it needs for testing.
Other useful tools include alligator clips and test leads. They help you connect the relay to the power supply and multimeter. With these tools, you’re ready for accurate relay tests.
Digital Multimeter Specifications
When picking a digital multimeter, focus on accuracy and resolution. A high sampling rate means more precise measurements. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Accuracy: ±0.5% to ±1% for most applications
- Resolution: 4-6 digits for high-precision measurements
- Sampling rate: 10-100 samples per second for fast and accurate measurements
Power Supply Requirements
A good power supply is essential for testing. Use a variable power supply to match the relay’s needs. If needed, your car’s battery can work too, but be careful to avoid damage.
Types of Relays and Their Test Parameters
Testing relays requires knowing the different types and their test needs. Single-Pole Single-Throw (SPST) relays are common and used in many places. They have four pins labeled 85, 86, 87, and 30. To get accurate results, specific test parameters are needed.
Other relays, like solid-state, reed, and electromechanical relays (EMRs), have their own special features. Solid-state relays are great for fast data scanning. EMRs, with more parts, are better for high power switching. Knowing these differences helps tailor your testing for the best results.
Important factors for relay testing include:
- Life expectancy: Reed relays last longer because they have fewer parts.
- Maximum switching volts: Voltage limits can be set by PCB trace spacing.
- Switch current: This is the max current a relay can handle without damage.
Considering these points and knowing each relay type’s test needs, you can get precise and dependable results. Whether it’s SPST or other relays, using the correct test parameters is key. Regular checks and upkeep can also spot relay issues early, reducing production downtime.
Direct Methods to Test a Relay
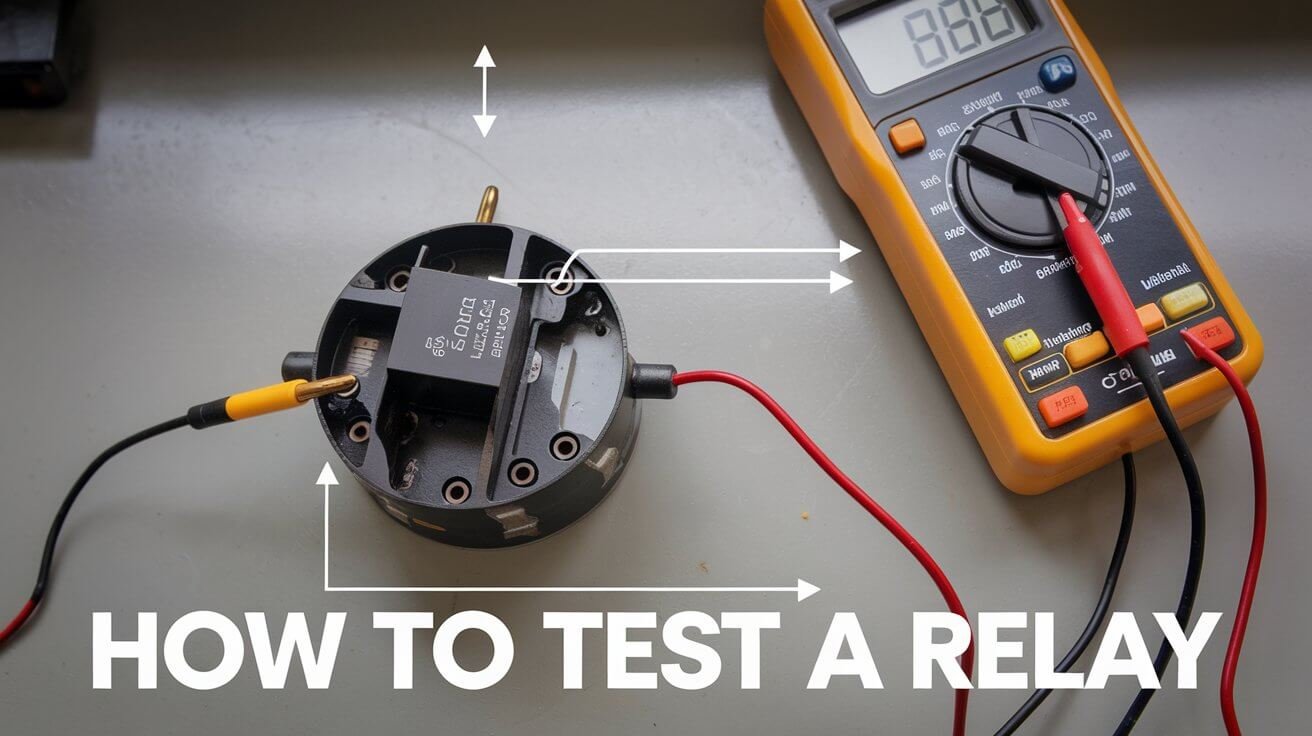
To check if a relay works right, you can use a few direct tests. These include checking resistance, voltage drop, and current flow. These methods help find and fix relay problems.
When testing resistance, measure between pins 85 and 86. The coil’s resistance should be between 50 and 200 ohms. Also, check for continuity between pins 87 and 30 when the relay is on.
Testing Procedures
Here’s how to test a relay:
- Measure the resistance between pins 85 and 86 to ensure it falls within the specified range.
- Check for continuity between pins 87 and 30 when the relay is energized.
- Perform voltage drop measurements to verify the relay is operating within the expected voltage range.
- Analyze the current flow to ensure it is within the specified limits, typically between 100 mA and 150 mA.
Analysis and Troubleshooting
After testing, you can spot relay problems. For instance, a high voltage drop or too much current flow means something’s wrong inside. Regular checks and upkeep can stop these issues and keep the relay running smoothly.
Common Relay Failure Signs
Identifying relay failure symptoms is key. Look for signs like no clicking sound when the relay is turned on. Also, check for continuity issues, like having continuity when you shouldn’t or not having it when you should.
Relays can fail due to many reasons. These include wrong wiring, short circuits, and too much voltage. These problems can make the relay not work right or fail completely. To fix it, check the circuit, the control circuit, and the relay coil and contacts for dirt.
Other signs of relay failure include the relay not working, not turning off, or acting strangely. This could be because of power problems, vibrations, or too much current. Knowing these signs and using tools like multimeters can help you find and fix relay problems fast.
| Relay Type | Failure Mode | Common Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Electromechanical Relays (EMRs) | Contact wear, coil failure | Excessive voltage, improper wiring, high-frequency operation |
| Solid State Relays | Overheating, electrical noise | Excessive current, high-frequency operation, inadequate heat sinking |
Knowing the common signs of relay failure and how to troubleshoot can help you fix problems quickly. This reduces downtime and makes your system more reliable.
Testing Automotive Relays
Testing automotive relays is key to keeping your car running right. These relays control important parts like horns, lights, and turn signals. You can use the car’s battery and a multimeter for this. The jump wire method is also helpful for finding relay problems.
It’s important to look at the car’s electrical system when testing relays. Relays switch circuits for high current needs. A multimeter can check if the relay works. For example, the resistance between pins 85 and 86 should be 50 to 120 ohms.
Battery Power Method
This method uses the car’s battery to power the relay. By connecting the multimeter, you can see voltage and current. This helps find relay or electrical system problems.
Jump Wire Technique
The jump wire technique is great for diagnosing relays. It bypasses the relay to check if the part works. This method can spot relay or wiring issues.
Circuit Testing Steps
To test the relay, follow these steps:
- Connect the multimeter to the relay
- Measure the voltage and current flow
- Use the jump wire technique to bypass the relay
- Check the controlled component for proper function
Following these steps and using the right techniques, you can effectively test automotive relays and diagnose issues with the car electrical system. Always be careful when working with electrical systems. If you’re unsure, get help from a professional.
| Pin Number | Function |
|---|---|
| 30 | Output |
| 85 | Coil |
| 86 | Coil |
| 87 | Output |
| 87a | Output (optional) |
Industrial Relay Testing Procedures
Testing industrial relays is different from testing automotive ones. They handle more voltage and current. This means you need to be extra careful and use special tools.
For industrial relays, you must think about a few things:
- Safety precautions: These relays can be dangerous if not handled right. So, it’s key to be careful to avoid harm or damage.
- Specialized testing equipment: You’ll need special tools like high-voltage testers and current injectors. These help mimic real-world conditions.
- Testing procedures: Testing these relays is different from other types. You must consider the system’s needs and the relay’s specific traits.
Following these steps and using the right tools, you can make sure your industrial relays work well and safely. This is important in any setting, whether it’s a factory or a regular place. Keeping them in good shape helps avoid problems and keeps things running smoothly.
| Relay Type | Testing Procedure | Specialized Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| Electromechanical Relay | Resistance testing, voltage drop measurements, and current flow analysis | Digital multimeter, power supply, and current injector |
| Solid-State Relay | Resistance testing, response time analysis, and voltage drop measurements | Digital multimeter, oscilloscope, and voltage source |
Relay Test Result Analysis
Understanding normal operating parameters for relays is key. A clear click when energized and correct continuity between pins show a relay works well. But, if a relay fails, it might show infinite resistance or no change in continuity, needing more checks.
It’s vital to interpret test results well for accurate relay checks. This means looking at the test data to see if the relay meets the needed standards. Knowing the test results helps you figure out if a relay needs to be replaced or if more tests are needed.
Normal Operating Parameters
Relays work right when they make a clear click when turned on, have the right continuity, and show the correct voltage and current. These standards can change based on the relay type and its use.
Failed Test Indicators
Signs of a failed relay include infinite resistance, no change in continuity when turned on, and unexpected voltage or current readings. These signs mean a relay has failed and might need to be replaced or checked more closely.
Relay diagnostics help spot problems by looking at test results. By understanding these results, you can make sure your relays are working right. This is very important in places where relay failure could cause big problems, like in power systems or industrial control systems.
| Test Parameter | Normal Operating Parameter | Failed Test Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| Clicking Sound | Clear clicking sound when energized | No clicking sound or unusual noise |
| Continuity | Proper continuity between switch pins | Infinite resistance or no change in continuity |
| Voltage and Current Readings | Expected voltage and current readings | Unexpected voltage or current readings |
Relay Maintenance Tips
Keeping your relays in good shape is key to their long life and reliable work. Regular cleaning and checks of relay contacts can stop small problems from becoming big ones. By taking care of your relays, you can cut down on failures and the need for new ones in your electrical systems.
To keep your relays working well, it’s important to clean the contacts and store them in a cool, dry place. This helps avoid corrosion. Here are a few easy steps to follow:
- Regularly check the relay contacts for wear or corrosion
- Clean the contacts with a soft brush or cotton swab
- Keep the relays in a cool, dry spot, away from too much heat or moisture
Following these tips and taking preventive steps, you can make your relays last longer and work better. Always handle your relays carefully. Avoid exposing them to too much heat, moisture, or dust.
| Relay Maintenance Tips | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Regular cleaning and inspection | Prevents minor issues from escalating into major failures |
| Storage in a dry, cool environment | Prevents corrosion and extends relay lifespan |
| Preventive care measures | Reduces frequency of failures and need for replacements |
Advanced Relay Diagnostics
For those who want to improve their relay testing skills, advanced diagnostic techniques are key. These methods use special tools like oscilloscopes to look at relay performance in more detail. With these tools, users can spot small problems in complex relay systems. This gives a better understanding of how relays work and when they might fail.
Some important parts of advanced relay diagnostics include:
- Using oscilloscopes to analyze switching times and contact bounce
- Validating correct function and logic settings in multifunction digital relays
- Applying simulated faults to mimic real-world scenarios through dynamic testing
- Utilizing output functions not designated for use after installation to prevent interference during testing
Using these advanced diagnostic methods and tools, users can make sure their complex relay systems work well. This is very important in today’s industrial and power systems, where things need to be reliable and accurate. With the right tools and techniques, users can find and fix problems early. This helps avoid big issues, cuts down on downtime, and boosts system performance.
| Diagnostic Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Oscilloscope Analysis | Using oscilloscopes to analyze relay performance and identify possible issues |
| Dynamic Testing | Applying simulated faults to mimic real-world scenarios and check relay settings |
| Output Function Testing | Using output functions not meant for use after installation to avoid interference during testing |
In Closing
Regular relay testing and maintenance are key for reliable electrical systems. This guide has shown you how to do it well. You can now check and keep relay systems in top shape, no matter the field.
Relay testing is vital for keeping electrical systems safe and working well. Keep honing your skills with these methods. This way, you’ll avoid sudden failures and make your systems run better.
Key Questions
What are the basic components of a relay?
A relay has a few key parts. These include the electromagnetic coil, contact points, and control circuit elements. Knowing these parts is key to testing a relay well.
What safety precautions should I take before testing a relay?
Safety first! Set up a safe area, use the right tools, and wear protective gear. These steps help avoid electrical hazards.
What tools are required for effective relay testing?
You’ll need a digital multimeter, a power source like a car battery, and tools like test leads and jumper wires. These are essential for testing.
Are there different types of relays, and do they require unique testing considerations?
Yes, there are many relay types, like SPST relays. Each needs its own test approach to get accurate results.
What are the common methods for directly testing a relay?
To test a relay, you can check resistance, measure voltage drops, and analyze current flow. These methods help find out if a relay works right.
How can I identify signs of relay failure?
Look out for odd noises, if it doesn’t respond, or if it acts strangely. Spotting these signs is key to fixing problems.
Are there any specific techniques for testing automotive relays?
Yes, for car relays, use the car battery and the jump wire method. This helps find issues in the car’s electrical system.
How do I interpret relay test results to determine if a relay is functioning properly?
To understand test results, know what’s normal for each relay type. Look for signs of failure. This skill helps decide if you need to replace a relay or not.
What are some best practices for maintaining relays to extend their lifespan?
Keep relays in good shape by cleaning contacts safely and storing them right. These steps can make your relays last longer.
What advanced diagnostic techniques can I use to analyze complex relay systems?
For detailed checks, use tools like oscilloscopes. They help spot small problems in complex systems.